Hi everyone,
welcome to my blog where I share my insights and tips on Azure networking. Today I want to talk about Azure Gateway Load Balancer, a new service that was recently announced by Microsoft. Azure Gateway Load Balancer is a SKU of the Azure Load Balancer portfolio that is designed for high performance and high availability scenarios with third-party network virtual appliances (NVAs). NVAs are software solutions that provide network functions such as firewalls, intrusion detection and prevention, traffic analytics, and more. With Azure Gateway Load Balancer, you can easily deploy, scale, and manage NVAs in your virtual network without any extra configuration or overhead.
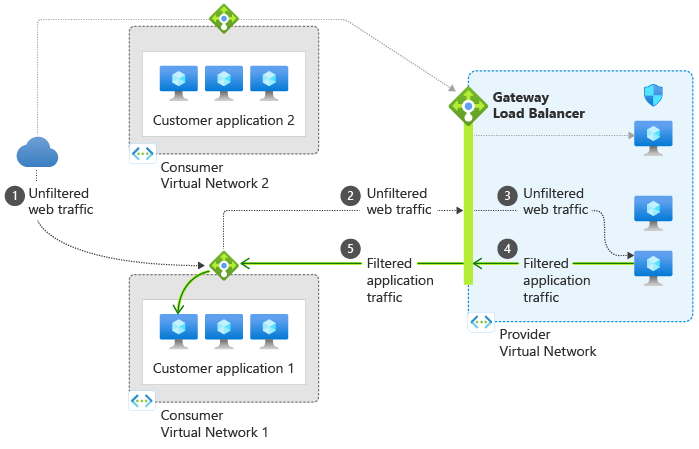
Azure Gateway Load Balancer works by creating a transparent network path between your public endpoint (such as a standard public load balancer or a virtual machine) and your NVAs. It ensures that all traffic to and from your endpoint is first sent to the NVAs before reaching your application. It also maintains flow stickiness and symmetry, meaning that packets traverse the same network path in both directions and NVAs that need this capability can function seamlessly. The health probe listens across all ports and routes traffic to the backend instances using the HA ports rule. Traffic sent to and from Azure Gateway Load Balancer uses the VXLAN protocol.
Azure Gateway Load Balancer has many benefits for scenarios that require advanced network functionality. For example, you can:
- Integrate NVAs transparently into the network path without changing your application or routing configuration.
- Easily add or remove NVAs in the network path without affecting availability or performance.
- Scale with ease while managing costs by using autoscaling and pay-as-you-go pricing models.
- Improve NVA availability by using zone-redundant deployment and automatic failover.
- Chain applications across regions and subscriptions by using a standard public load balancer or a standard IP configuration of a virtual machine as your public endpoint.
To use Azure Gateway Load Balancer, you need to create a virtual network with two subnets: one for your backend pool of NVAs (the provider subnet) and one for your bastion host (the consumer subnet). You also need to create a network security group with the necessary rules to allow traffic between the subnets and the gateway load balancer. Then you can create a gateway load balancer with a private frontend IP configuration and a load balancing rule that maps it to the backend pool of NVAs. Finally, you can chain your public endpoint to the gateway load balancer by selecting it as the next hop type in the route table of your consumer subnet.
If you want to learn more about Azure Gateway Load Balancer and how to create one using the Azure portal, you can check out this tutorial: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/load-balancer/tutorial-gateway-portal
I hope you found this blog post useful and interesting. If you have any questions or feedback, please leave them in the comments section below.
Thanks for reading and happy networking!
